In the world of fabric and fashion, Nahttypen—or seam types—are the invisible architecture behind every garment and textile product. Whether you’re a professional fashion designer, a technical textile engineer, or an enthusiastic DIY hobbyist, mastering seam types is key to combining durability, aesthetics, and innovation in fabric construction.
This comprehensive guide explores everything from the basics of Nahttypen, their functional and aesthetic roles, traditional and modern seam types, cutting-edge innovations, and practical guidance for implementation in various industries. Let’s stitch this knowledge together—one seam at a time.
What Are Nahttypen and Why Do They Matter?
To put it simply, Nahttypen refers to various methods of joining fabric pieces together. But in practice, the choice of a seam impacts:
- Structural strength
- Comfort and flexibility
- Water or weather resistance
- Garment silhouette
- Visual appeal
Seams are no longer just stitching—they’re a blend of art, science, and innovation. Picking the right seam type is often the difference between a product that lasts and one that fails.
Historical Evolution of Seam Types:
- Prehistoric Beginnings: Early humans used bone needles and sinew to sew animal hides, laying the foundation for basic seam construction.
- Medieval Tailoring Guilds: Skilled artisans in Europe formalized sewing techniques and introduced structured garment seams through hand stitching.
- Industrial Revolution: The invention of sewing machines enabled mass production of garments, standardizing many classic seam types.
- 20th-Century Fashion & Function: Seam types expanded to support new fabric technologies, including stretch and synthetic materials for fashion and uniforms.
- 21st-Century Innovations: Modern Nahttypen now include bonded seams, CAD-guided patterns, and ultrasonic welding for performance gear and technical textiles.
Key Functions of Nahttypen:
Structural Integrity:
Nahttypen play a crucial role in holding fabric pieces together securely. In garments like uniforms, jackets, and upholstery, seams must withstand tension, repeated movement, and daily wear. The right seam type ensures the garment doesn’t tear or fall apart, especially in stress areas like underarms, shoulders, or seat seams.
Design Definition:
Seams aren’t just for construction—they shape the garment’s overall silhouette. Strategic seam placement helps contour fabric around the body, creating structure and form. From fitted dresses to tailored suits, seam types and positions determine how clothing fits, flows, and appears, making them vital for both aesthetics and fashion design.
User Comfort:
The right Nahttyp enhances comfort by reducing chafing, irritation, and seam pressure on the skin. Especially in activewear, underwear, or lingerie, flat or soft seams allow the body to move freely without discomfort. Seam choice and placement can dramatically impact the wearer’s experience, particularly during physical activity or long wear.
Functional Features:
Modern seams offer much more than fabric connection—they enhance functionality. Depending on the construction, seams can provide waterproof barriers, flexibility for stretch garments, or breathability in ventilated areas. Performance gear, sportswear, and technical fabrics rely heavily on specialized seam types to meet environmental or movement-specific requirements.
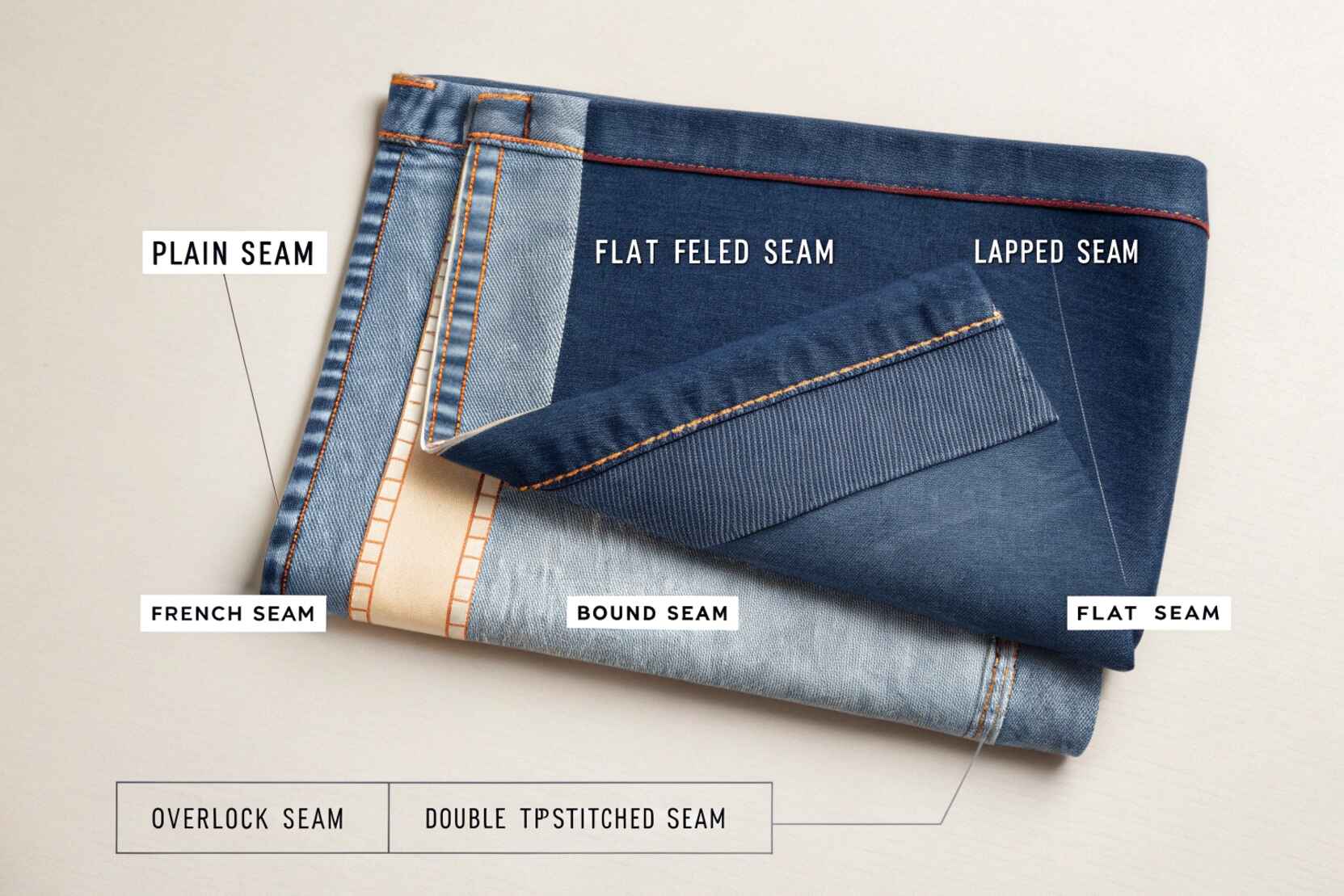
Core Categories of Nahttypen:
Here’s a breakdown of the most widely used Nahttypen, their construction, advantages, and ideal uses.
Plain Seam (Einfache Naht):
The foundational seam in sewing. Two pieces of fabric are joined with a single line of straight stitching.
- Best for: Shirts, trousers, home textiles
- Pros: Simple, versatile, time-efficient
- Cons: Exposed edges need finishing
Flat-Felled Seam (Flachnaht):
A double-stitched seam with enclosed raw edges, folded flat for maximum durability.
- Used in: Jeans, uniforms, heavy-duty garments
- Strengths: Strong, clean, prevents fraying
- Challenges: Bulky, time-intensive
French Seam (Französische Naht):
A seam that hides raw edges between two stitching lines.
- Ideal for: Sheer, delicate fabrics like silk and chiffon
- Pros: Elegant finish, inside-out neatness
- Cons: Not suitable for thick materials
Bound Seam (Besetzte Naht):
Fabric edges are enclosed in a separate bias strip.
- Great for: Raincoats, designer fashion, outerwear
- Advantages: Durable, stylish
- Downside: Requires more time and materials
Lapped Seam (Überlappnaht):
One fabric edge overlaps the other and is topstitched.
- Common in: Leather jackets, canvas products
- Strengths: Visually striking, robust
- Drawbacks: Bulkier, visible seamline
Flat Seam (Flachnaht):
Fabric edges are joined edge-to-edge for a flat surface.
- Perfect for: Sportswear, activewear, base layers
- Benefits: Lightweight, chafe-free
- Weaknesses: Less tensile strength
Overlock Seam (Overlocknaht):
Done with an overlock machine that trims, sews, and finishes edges simultaneously.
- Applications: Knitwear, t-shirts, stretch fabrics
- Pros: Speed, stretch, edge finishing
- Cons: Needs special machine
Double-Topstitched Seam:
Two parallel topstitches reinforce and stylize a seam.
- Used in: Denim, fashion accents
- Upside: High durability and visual interest
- Limitation: Not suitable for lightweight fabrics
Modern Innovations in Nahttypen:
Seam Taping:
Seam taping involves applying heat-activated adhesive tape over stitched seams to make them waterproof. This technique prevents water from seeping through needle holes, ensuring protection in wet conditions. It’s widely used in outdoor jackets, military uniforms, and sportswear where moisture resistance is critical for both performance and comfort.
Bonded Seams:
Bonded seams replace traditional stitching with adhesive layers that fuse fabric together. They create smooth, flat, and stretchable seams that are both waterproof and lightweight. Common in rainwear, wetsuits, and compression garments, these seams eliminate bulk while enhancing flexibility and performance—ideal for modern, high-tech or form-fitting clothing.
Ultrasonic Welding:
This method uses high-frequency sound waves to fuse synthetic fabrics together without using thread or needles. It’s fast, produces strong bonds, and creates clean, smooth seams. Ultrasonic welding is perfect for sterile or technical textiles like medical clothing, as it minimizes perforation and enhances durability, especially in synthetic fibers.
Laser Cutting & Heat Sealing:
Laser cutting allows precise shaping of fabric edges, while heat sealing bonds those edges seamlessly without stitching. This innovation improves the appearance and functionality of seams by reducing fraying and ensuring clean lines. It’s especially valuable in performance textiles, where precision, smooth finishes, and durability are key priorities.
Technical Factors in Seam Construction:
When choosing or designing Nahttypen, consider:
- Fabric Type: Choose seams based on fabric behavior—stretch fabrics need flexible seams like flatlock, while woven fabrics benefit from stable seams like plain or French seams.
- Thread Strength: Use polyester for durability and stretch, cotton for softness, and nylon for resilience in high-stress seams.
- Seam Allowance: The extra fabric margin affects seam strength and stability; too narrow may weaken the seam, too wide may cause bulk.
- Stitch Length: Shorter stitches offer strength on delicate fabrics; longer stitches allow flexibility but may reduce hold on stress points.
- Finishing Techniques: Use pinking shears, serging, or binding to prevent fraying and extend seam life, especially on raw edges.
Nahttypen in Industry Applications:
Fashion Design:
In fashion, precise seam types help shape the garment’s silhouette, control fabric drape, and define stylistic lines. Whether it’s a structured jacket or a flowing dress, seam choice directly affects both the fit and aesthetics. Designers often use decorative or hidden seams to complement the fabric and enhance visual appeal.
Medical Textiles:
Seams in medical garments must meet strict hygiene and comfort standards. Seamless or bonded construction prevents bacteria buildup and reduces skin irritation. These seams are commonly used in surgical gowns, compression garments, and hospital wear where cleanliness, antimicrobial properties, and ease of movement are essential for patient and professional use.
Outdoor Gear:
For outdoor clothing and equipment, seam performance is critical. Taped and bonded seams are used to prevent water entry and retain insulation. Jackets, sleeping bags, and tents rely on these seam types for waterproofing, wind resistance, and thermal efficiency—ensuring users stay dry and comfortable in harsh environmental conditions.
Interior Design:
In interior applications, seams play a decorative and functional role. Whether on curtains, cushions, or upholstered furniture, seam types influence style, strength, and edge finishing. Topstitched or piped seams are often used to add texture and enhance design while reinforcing the durability of fabric in high-use home environments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Seam Construction:
- Using the Wrong Seam Type for Fabric Weight: Pairing heavy fabrics with delicate seams—or vice versa—can cause puckering, tearing, or an unbalanced garment. Always match seam strength to fabric type.
- Overstretching While Stitching: Pulling fabric while sewing can distort seams, causing ripples or breakage. Let the machine feed the fabric naturally to maintain shape.
- Poor Edge Finishing: Leaving raw edges unfinished can lead to fraying and reduced garment lifespan. Always finish seams with serging, binding, or pinking where needed.
- Inadequate Seam Allowances: Too little allowance weakens seams; too much creates bulk. Follow standard seam allowance guidelines for your fabric and pattern.
- Misalignment or Off-Grain Seams: Sewing off the grain causes twisting and poor fit. Ensure fabric pieces are cut and stitched along the correct grain line.
How Can You Extend the Life of Seams in Garments?
Use Gentle Washing Cycles:
Always wash garments with delicate seams using gentle cycles to avoid stress on the threads. Strong agitation or harsh detergents can weaken both fabric and stitching. Mild washing not only preserves the fabric quality but also maintains seam integrity, ensuring your clothes stay intact and comfortable for longer use.
Avoid Bleach and High Heat:
Bleach and high-temperature drying can damage threads, especially in synthetic or blended fabrics. Bleach breaks down fibers, while excessive heat can melt or shrink them. To keep seams durable and garments wearable, air-dry when possible and use mild detergents. Low-temperature settings protect seam construction and extend garment lifespan effectively.
Make Prompt Repairs:
Ignoring small seam tears can lead to bigger damage over time. Fixing loose threads or fraying early helps avoid full seam splits or structural failure. Use a matching thread and a secure stitch type. Regular maintenance like this keeps garments in good condition and extends their usability with minimal effort.
Reinforce High-Stress Zones:
Areas that undergo frequent tension, like underarms, knees, or pockets, need reinforced seams. Double stitching or using stronger seam types prevents ripping. Reinforcement adds longevity, especially in activewear or daily-use items. Taking this proactive step enhances overall garment durability, making it better suited for long-term or intense wear.
Expert Tips for Choosing the Right Nahttyp:
- Assess Fabric Needs: Match the seam to the fabric’s weight and flexibility. Use enclosed seams for delicate materials and reinforced seams for heavy or stretch fabrics to ensure strength, proper drape, and long-term durability in every finished piece.
- Evaluate Garment Function: Consider how the garment will be worn. Activewear needs stretchable seams; rainwear requires waterproofing. Choose a seam that supports the intended activity, environmental exposure, and durability based on actual usage.
- Prioritize Aesthetics: Seams influence design. Choose decorative or visible seam types like topstitching for stylish details, or invisible seams for sleek finishes. Make sure the seam’s appearance complements the overall garment look and purpose.
- Check Skill Requirements: Some seams are easy, others complex. Overlock, flatlock, or bonded seams need specific tools and experience. Pick seam types that match your skill level and equipment to avoid construction issues or poor results.
- Balance Form and Function: The best seam choice balances visual appeal with practicality. A seam should enhance the garment’s look while providing necessary performance features like flexibility, insulation, or water resistance depending on the project’s goals.
Future Trends in Seam Technology:
Seam technology is rapidly evolving to meet the demands of smart, sustainable, and efficient fashion. Smart seams now feature embedded conductive threads, enabling integration with wearable tech for health monitoring or connectivity. Biodegradable stitching is gaining traction as eco-conscious brands seek compostable alternatives to synthetic threads, promoting sustainable fashion practices.
Meanwhile, AI-assisted seam design leverages CAD software and machine learning to optimize seam placement, reduce waste, and improve fit during prototyping. These innovations are transforming not just how garments are made, but also how they function and impact the environment.
FAQs:
1. Can I combine different seam types in one garment?
Yes, combining seam types is common in advanced sewing. For example, use flat-felled seams in high-stress areas like shoulders, and French seams in delicate parts like sleeves. Blending seam styles lets you optimize both strength and appearance based on each section of the garment.
2. What seam types are best for reversible clothing?
Reversible garments require seams that look clean on both sides. Flat-felled and French seams are ideal because they enclose raw edges completely, offering a polished finish regardless of which side is facing out. Avoid bulky seams that could affect the garment’s drape
3. How do different seam types affect fabric waste?
Some seams, like bound or flat-felled seams, use more fabric due to folding or binding. Plain seams use less fabric but may require additional finishing. If you’re aiming for zero-waste or sustainable sewing, consider seam styles that minimize offcuts and bulk.
4. Do seam types influence garment breathability?
Yes, especially in performance wear. Flat seams and overlock seams allow better airflow due to their low profile, enhancing comfort during physical activity. In contrast, bonded or taped seams can reduce breathability but improve water resistance, so balance is key depending on usage.
5. What’s the best seam type for beginner sewing projects?
Plain seams are perfect for beginners—easy to sew, quick to learn, and suitable for most basic fabrics. Pair them with simple finishing techniques like zigzag or pinked edges to prevent fraying without needing special tools or advanced skills.
Conclusion:
Nahttypen are far more than functional stitching—they are the design backbone and performance driver of every textile product. From the earliest hand-sewn seams to today’s AI-enhanced, bonded, and ultrasonic technologies, seam types continue to shape how we create, wear, and experience garments.
Choosing the right seam type isn’t just about sewing—it’s about durability, style, innovation, and purpose. Whether you’re tailoring couture, crafting activewear, or designing for sustainability, understanding Nahttypen empowers you to elevate both form and function with every stitch. Seam by seam, it’s how quality garments are truly made.
Related post:







